The thyroid is a small, butterfly-shaped gland at the base of the neck. Despite its size, it plays a crucial role in regulating metabolism, energy levels, and overall hormonal balance. When the thyroid doesn’t function properly, it can lead to a range of health issues, including symptoms related to an abnormal thyroid. In this article, we’ll explore the different types of thyroid disorders, their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
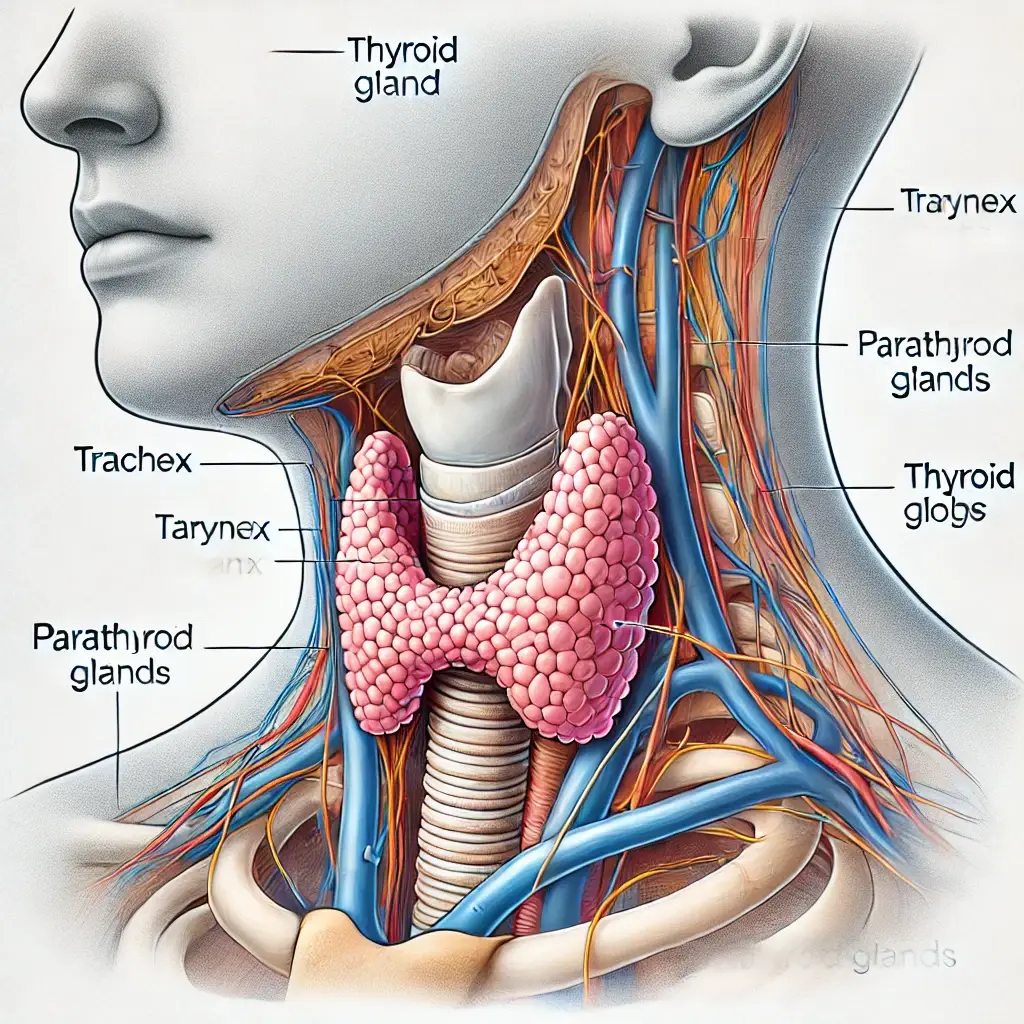
Table of Contents
Understanding abnormal thyroid function is essential for identifying potential health risks and ensuring timely treatment.
What is the Thyroid and Its Role in the Body?
The thyroid gland produces hormones that influence nearly every organ in the body. It controls metabolism, heart rate, digestion, and even mood. When functioning correctly, it keeps the body’s processes running smoothly. However, when the thyroid becomes overactive or underactive, it can disrupt multiple bodily functions, leading to significant health concerns.
Common Types of Thyroid Disorders
Thyroid issues can manifest in different ways. Here are the most common types:
| Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid) | Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid) |
| Hypothyroidism occurs when the thyroid gland doesn’t produce enough hormones, slowing down the body’s functions. Common symptoms include fatigue, weight gain, cold intolerance, dry skin, and depression. It’s often caused by Hashimoto’s thyroiditis, an autoimmune condition. | Hyperthyroidism happens when the thyroid produces too much hormone, speeding up the body’s metabolism. Symptoms include weight loss, rapid heartbeat, anxiety, excessive sweating, and tremors. Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. |
Goiter (Thyroid Enlargement)
A goiter is an abnormal enlargement of the thyroid gland, which may be caused by iodine deficiency or hormonal imbalances. While some goiters are harmless, others can lead to difficulty breathing or swallowing.
Thyroid Nodules and Tumors
Thyroid nodules are lumps that form within the gland. While most are benign, some can be cancerous. Regular check-ups and imaging tests help determine their nature and whether treatment is needed.
Thyroiditis (Inflammation of the Thyroid)
Thyroiditis refers to inflammation of the thyroid gland, which can lead to either hyperthyroidism or hypothyroidism. It may be caused by infections, autoimmune conditions, or certain medications.
Causes of Abnormal Thyroid Function
Thyroid disorders can be triggered by various factors, including genetic predisposition, autoimmune diseases, iodine deficiency, stress, and certain medical treatments. Understanding these causes can help in early detection and prevention.
Signs and Symptoms of Thyroid Disorders
The symptoms of thyroid disorders vary depending on whether the gland is overactive or underactive. Some common signs include:
- Hypothyroidism: Fatigue, weight gain, dry skin, hair thinning, and slow heart rate.
- Hyperthyroidism: Unintentional weight loss, palpitations, anxiety, and excessive sweating. If you experience persistent symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider.
Diagnosis and Testing for Thyroid Issues
Doctors diagnose thyroid disorders using:
- Physical Examination: Checking for swelling or nodules in the neck.
- Blood Tests: Measuring levels of TSH (thyroid-stimulating hormone), T3, and T4 hormones.
- Imaging Tests: Ultrasound and radioactive iodine uptake scans help assess the structure and function of the thyroid gland.
Treatment Options for Thyroid Disorders
The treatment approach depends on the specific thyroid disorder.
Medications and Hormone Therapy
- Hypothyroidism: Treated with synthetic thyroid hormone (levothyroxine) to restore normal levels.
- Hyperthyroidism: Managed with anti-thyroid medications like methimazole or beta-blockers to control symptoms.
Diet and Lifestyle Changes
A balanced diet rich in iodine, selenium, and zinc supports thyroid health. Stress management, regular exercise, and avoiding processed foods can also help regulate thyroid function.
Surgical and Radioactive Treatments
- Surgery: In cases of large goiters, nodules, or thyroid cancer, part or all of the thyroid may be surgically removed.
- Radioactive Iodine Therapy: Used to shrink an overactive thyroid in hyperthyroidism cases.
Complications of Untreated Thyroid Disorders
Ignoring thyroid issues can lead to severe complications, such as heart disease, infertility, osteoporosis, and even a life-threatening condition called myxedema (severe hypothyroidism) or thyroid storm (severe hyperthyroidism). Early detection and treatment are crucial.
Prevention and Long-Term Management
While some thyroid conditions are unavoidable due to genetics, others can be managed through:
- Regular Check-ups: Early detection helps prevent severe complications.
- Healthy Diet: Including iodine-rich foods like fish, dairy, and eggs.
- Stress Reduction: Yoga, meditation, and proper sleep improve hormonal balance.
Conclusion
Thyroid disorders are common but manageable with proper diagnosis and treatment. Being aware of the symptoms and taking preventive steps can ensure better thyroid health and overall well-being. If you suspect a thyroid issue, consult a healthcare provider for appropriate testing and treatment.